We’ve written recently about how to speed up jenkins builds so that you can accelerate your CICD pipeline when running Jenkins Docker workloads. In this post, we will deploy a fault-tolerant Jenkins service using Docker Swarm backed by Portworx volumes. You can view a demo video here: https://youtu.be/tH0Et7iEQ04.
First, let’s get an overview of our setup.
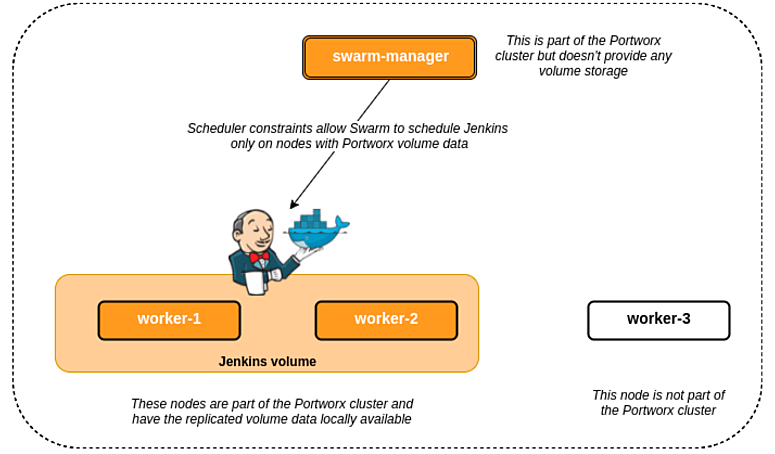
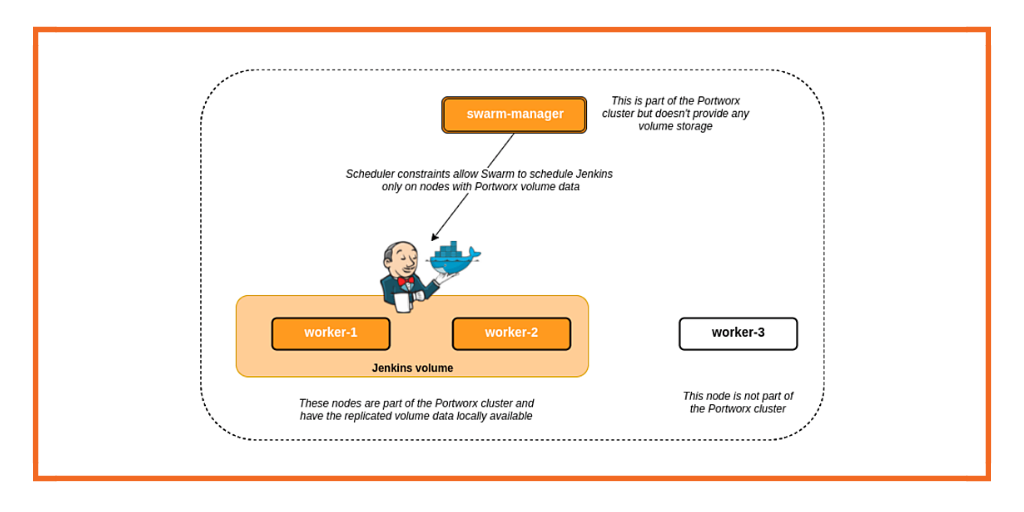
Above, you can see;
- A Docker Swarm cluster with one manager and three worker nodes
- Portworx will be installed on the manager (Swarm-manager) and two of the worker nodes (worker-1 and worker-2)
- A shared, replicated Portworx volume will be used by the Jenkins instances for the jenkins home directory.
Let’s dive right into it and see how we set up our HA Jenkins Docker environment !
Creating a Swarm cluster
On swarm-master:
$ docker swarm init |
On worker-1, worker-2 and worker-3, use the join command given in output of swarm init command.
docker swarm join --token <token> <swarm-manager-ip>:2377 |
Check Swarm status.
swarm-master $ docker node ls ID HOSTNAME STATUS AVAILABILITY MANAGER STATUS olhjma1360dqu6331gh8bwfba worker-2 Ready Active olmsb9upmzcgk6kusb4iv58fz worker-3 Ready Active py8sz1oh7yxkj5bnjol1nx5r6 * swarm-master Ready Active Leader qzc2i4qtf6iox8rtsi9kq0xq6 worker-1 Ready Active |
Creating a Portworx volume for Jenkins Docker application
Install Portworx on the swarm-manager, worker-1 and worker-2. Detailed installation steps can be found here. In this demo, we don’t give any devices to the Portworx node running on Swarm manager.
Create a volume.
$ pxctl volume create --shared --repl 2 --size 4 jenkins_vol Shared volume successfully created: 554257905897367936 |
The volume should have it’s data replicated to 2 nodes which can be seen in below output.
$ pxctl volume inspect jenkins_vol Volume : 554257905897367936 Name : jenkins_vol Size : 4.0 GiB Format : ext4 HA : 2 IO Priority : LOW Creation time : Apr 17 20:41:16 UTC 2017 Shared : yes Status : up State : detached Reads : 0 Reads MS : 0 Bytes Read : 0 Writes : 0 Writes MS : 0 Bytes Written : 0 IOs in progress : 0 Bytes used : 129 MiB Replica sets on nodes: Set 0 Node : 192.168.56.102 Node : 192.168.56.103 |
Create a Swarm service for Jenkins
$ docker service create --name jenkins \ --publish 8082:8080 \ --publish 50000:50000 \ -e JENKINS_OPTS="--prefix=/jenkins" \ --reserve-memory 300m \ --mount "type=volume,source=jenkins_vol,target=/var/jenkins_home" \ --constraint 'node.labels.jenkins_vol == true' \ jenkins |
- Notice how we mount the jenkins home directory to the Portworx volume
- We also specify a scheduler constraint which instructs Swarm to schedule Jenkins container only on nodes which have a label for our volume. This will result on Jenkins having local access to volume data leading to great performance.
$ docker service ps jenkins ID NAME IMAGE NODE DESIRED STATE CURRENT STATE ERROR PORTS j7e967ux3n5n jenkins.1 jenkins:latest worker-2 Running Running 2 seconds ago |
Observe the node on which Jenkins is running & perform initial Jenkins setup by going to http://<node-ip>:8082/jenkins. Create a test project and run some builds!
Test failover by killing Swarm worker node
Find the worker which is running the Jenkins container and drain it.
swarm-master $ docker node update --availability drain worker-2 worker-2 |
Observe that Jenkins will now run on the other worker which has the Portworx volume. This is because of the –constraint we specified while creating the service. Without the constraint, Jenkins could have been scheduled on any other node in the Swarm cluster.
swarm-master $ docker service ps jenkins ID NAME IMAGE NODE DESIRED STATE CURRENT STATE ERROR PORTS 4nt0ppc6x81z jenkins.1 jenkins:latest worker-1 Running Running 2 seconds ago j7e967ux3n5n \_ jenkins.1 jenkins:latest worker-2 Shutdown Shutdown 3 seconds ago |
Access Jenkins on the new worker node and observe that all our data is still intact!
In a production scenario, the Swarm worker nodes can be fronted by a load balancer or a service discovery which directs the Jenkins requests to the node running the container.
Harsh Desai
Member of Technical Staff
Portworx
Like what you read? Learn more about Docker storage, Kubernetes storage and DC/OS storage.
Share
Subscribe for Updates
About Us
Portworx is the leader in cloud native storage for containers.
Thanks for subscribing!

Harsh Desai
Portworx | Member of Technical StaffExplore Related Content:
- ci/cd